
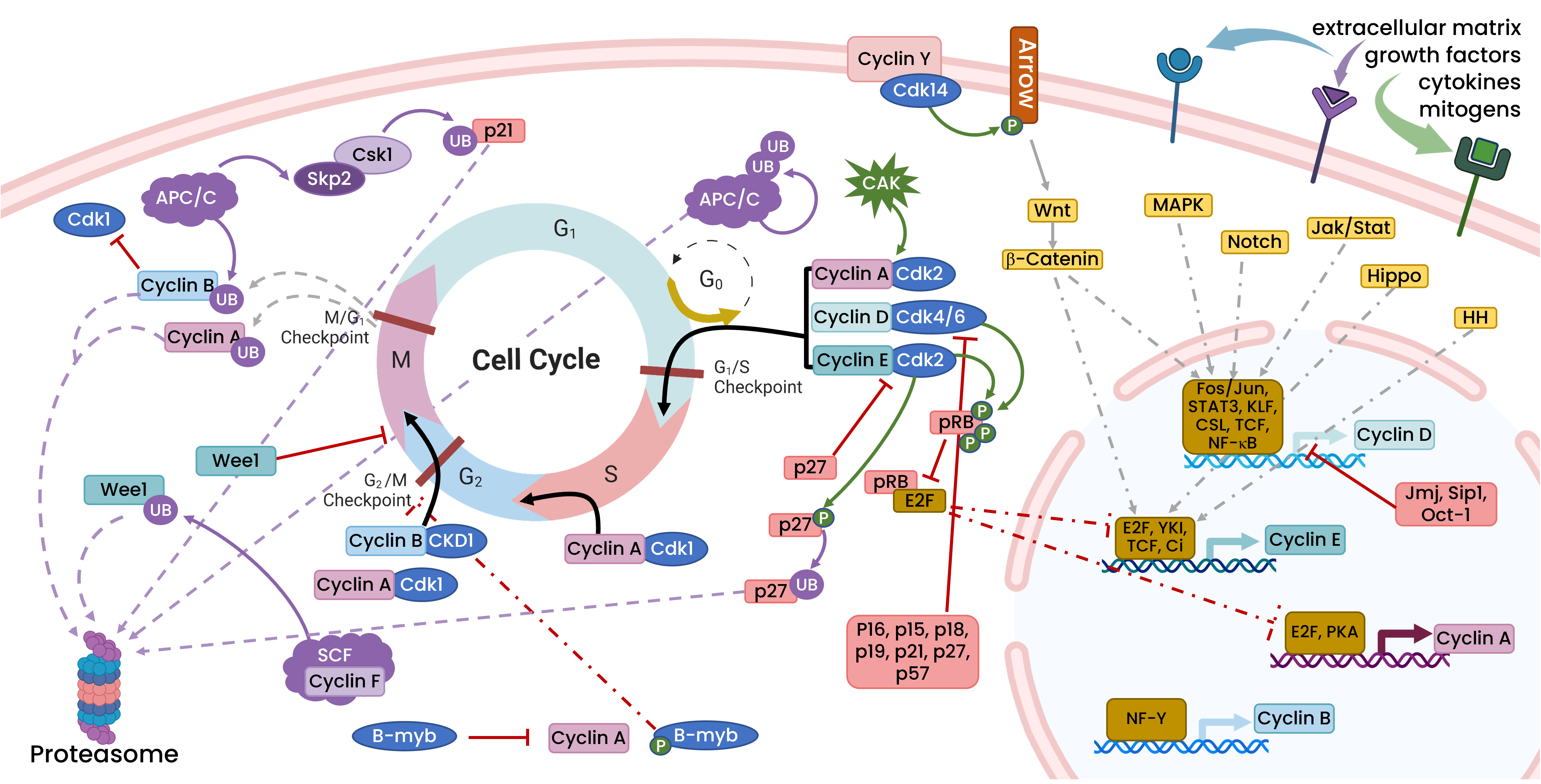
The cell cycle and its master regulators. Schematic representation of
The second approach to understanding cell cycle regulation was the genetic analysis of yeasts, pioneered by Lee Hartwell and his colleagues in the early 1970s.Studying the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, these investigators identified temperature-sensitive mutants that were defective in cell cycle progression.The key characteristic of these mutants (called cdc for cell division cycle.

Proteins That Regulate The Cell Cycle We Are Eaton
They are implicated in essential cellular functions such as transcription, DNA damage repair, epigenetic regulation, metabolism, proteolytic degradation, stem cell self-renewal, neuronal functions, and spermatogenesis. Figure 28.13.1 28.13. 1 shows the cell cycle and the involvement of CDKs/cyclins at key points.
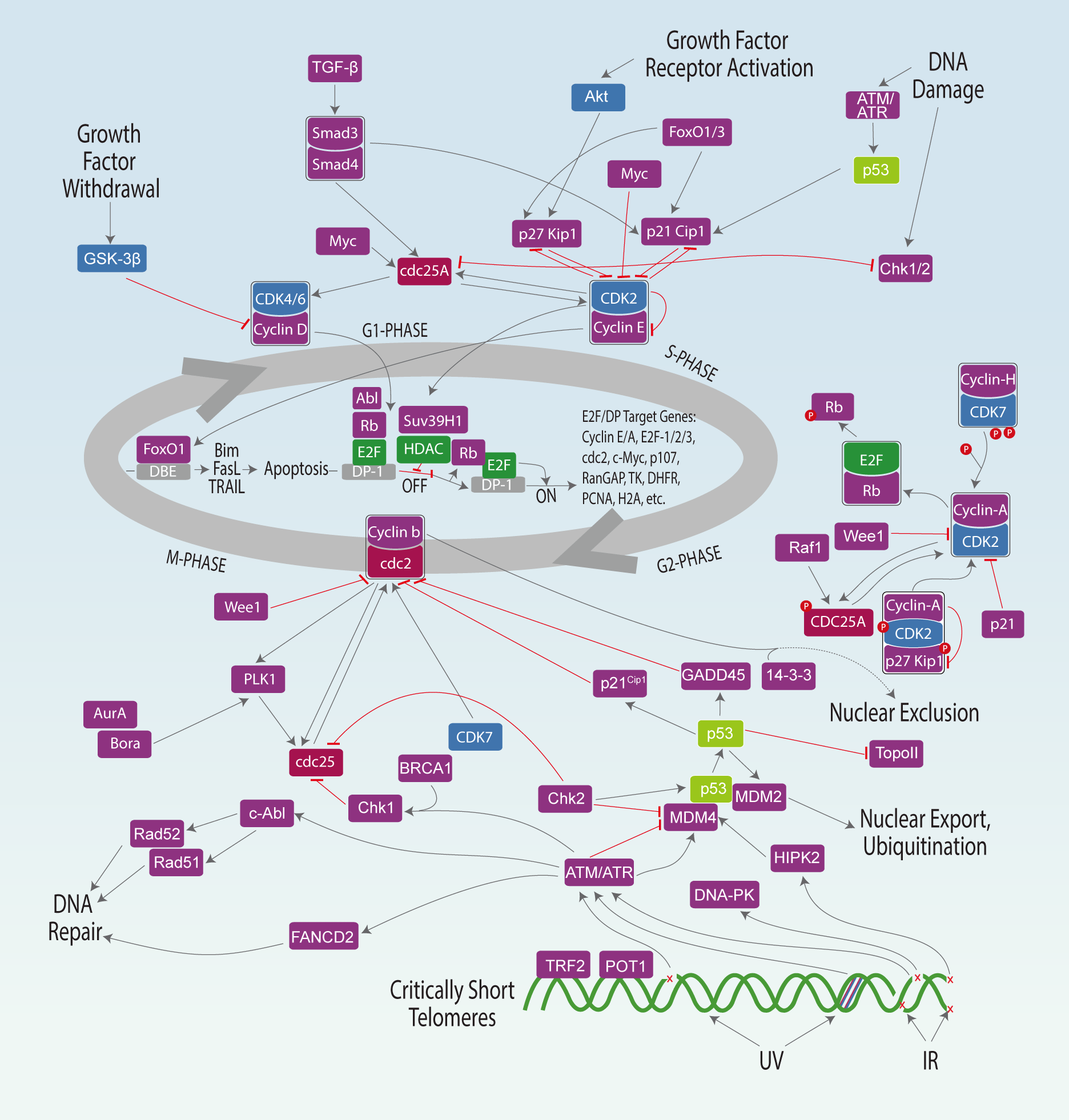
Cell Cycle Signaling Pathway AbMole BioScience
Cell cycle control primarily governed through the number of CDKs, cyclins, cell cycle signaling pathways, and checkpoints of cell cycle all of which are discussed in this chapter, we will also go over how the cell cycle progresses through different stages. The fundamental regulator of cell cycle advancement is CDKs.
PPT Ch. 8 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
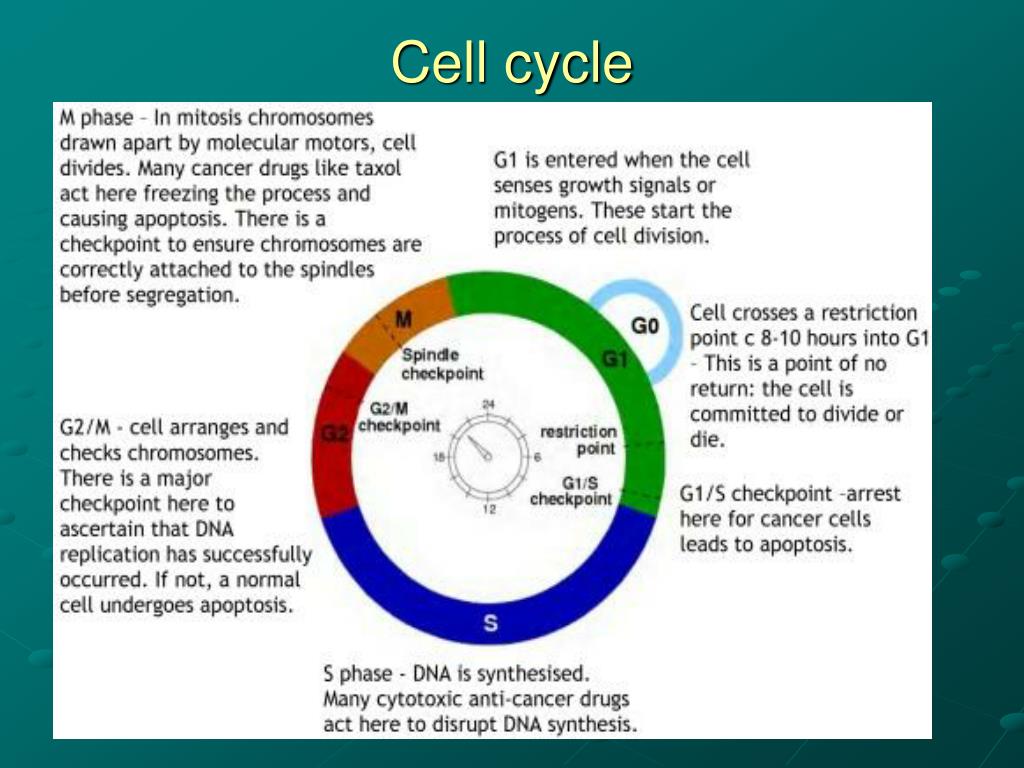
1. The G 1 Checkpoint. The G 1 checkpoint controls the transition from the G 1 to the S phase of the cell cycle. If actively dividing cells (e.g., stem cells) in G 1 fail to complete their preparation for replication, the S-phase kinase won't be produced and the cells won't proceed the S phase until the preparatory biochemistry catches up with the rest of the cycle.

Cell Cycle Regulation
A protein called Pom1 localizes to the tips of the cell and halts cell cycle progression via regulation of the Cdr1-Cdr2-Wee1-Cdc2 axis, which is centrally placed in a region called the interphase node. At longer cell lengths, Pom1 can no longer influence this complex, and the cell cycle can progress to M phase [33, 34].

Phases Of A Cell Cycle
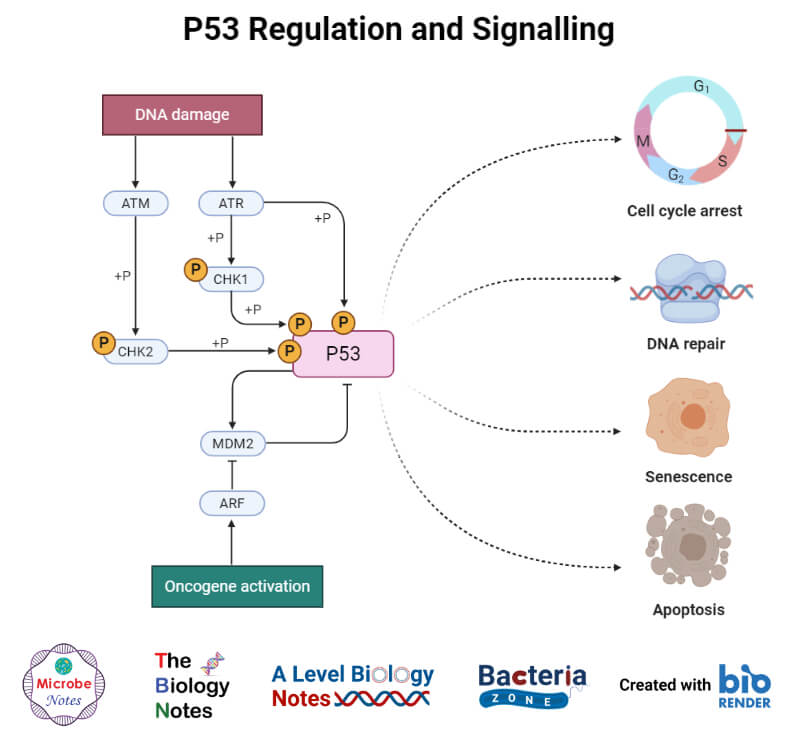
Negative Regulation of the Cell Cycle. The second group of cell cycle regulatory molecules are negative regulators. Negative regulators halt the cell cycle. Remember that in positive regulation, active molecules cause the cycle to progress. The best understood negative regulatory molecules are retinoblastoma protein (Rb), p53, and p21.

Schematic overview of proteins involved in the control of cell cycle
The second group of cell-cycle regulatory molecules are negative regulators, which stop the cell cycle. Remember that in positive regulation, active molecules cause the cycle to progress. The best understood negative regulatory molecules are retinoblastoma protein (Rb) , p53, and p21. Retinoblastoma proteins are a group of tumor suppressor.
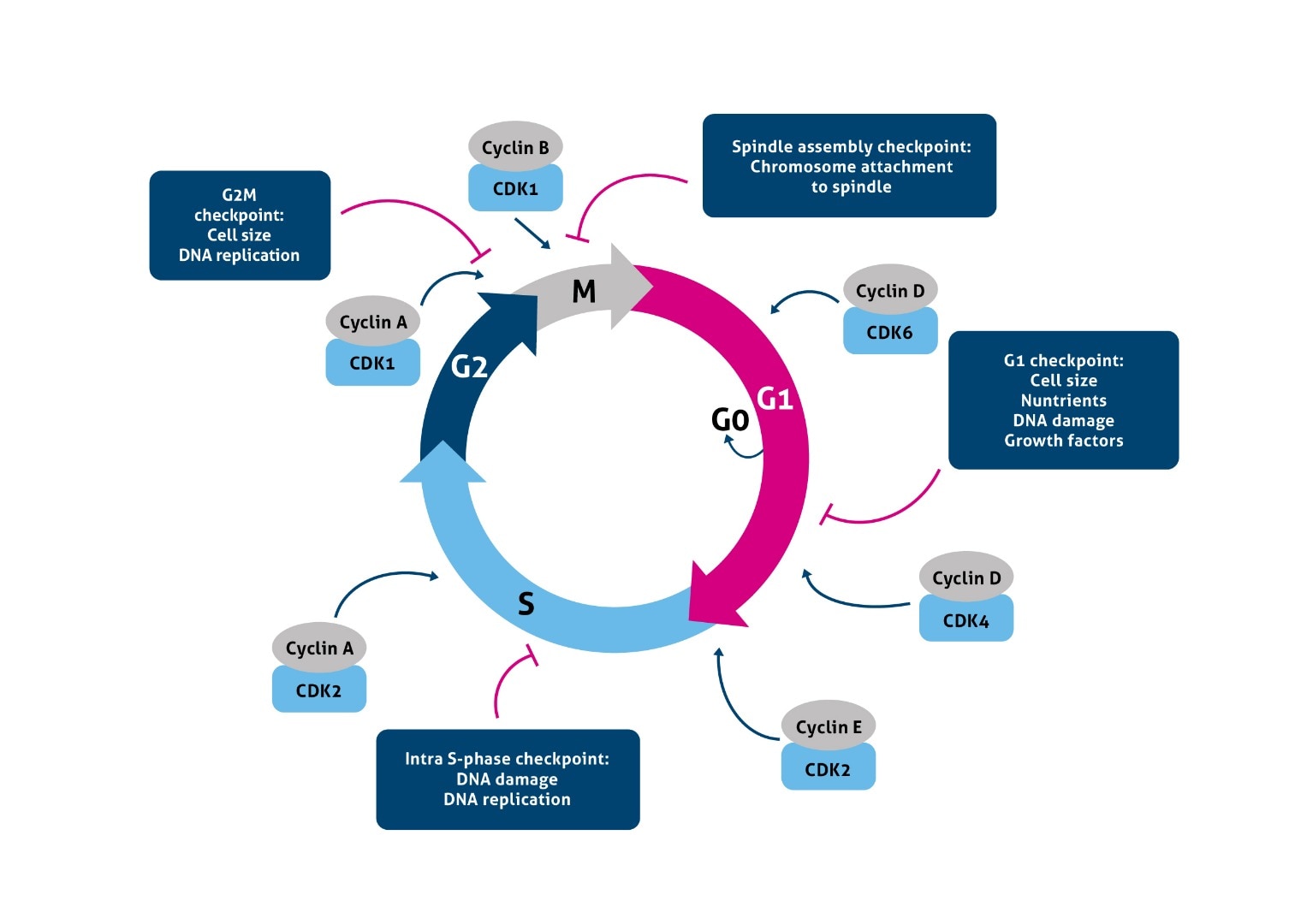
7 Explain Two Different Proteins Involved in Cell Cycle Control Clay
In order to drive the cell cycle forward, a cyclin must activate or inactivate many target proteins inside of the cell. Cyclins drive the events of the cell cycle by partnering with a family of enzymes called the cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks). A lone Cdk is inactive, but the binding of a cyclin activates it, making it a functional enzyme and.
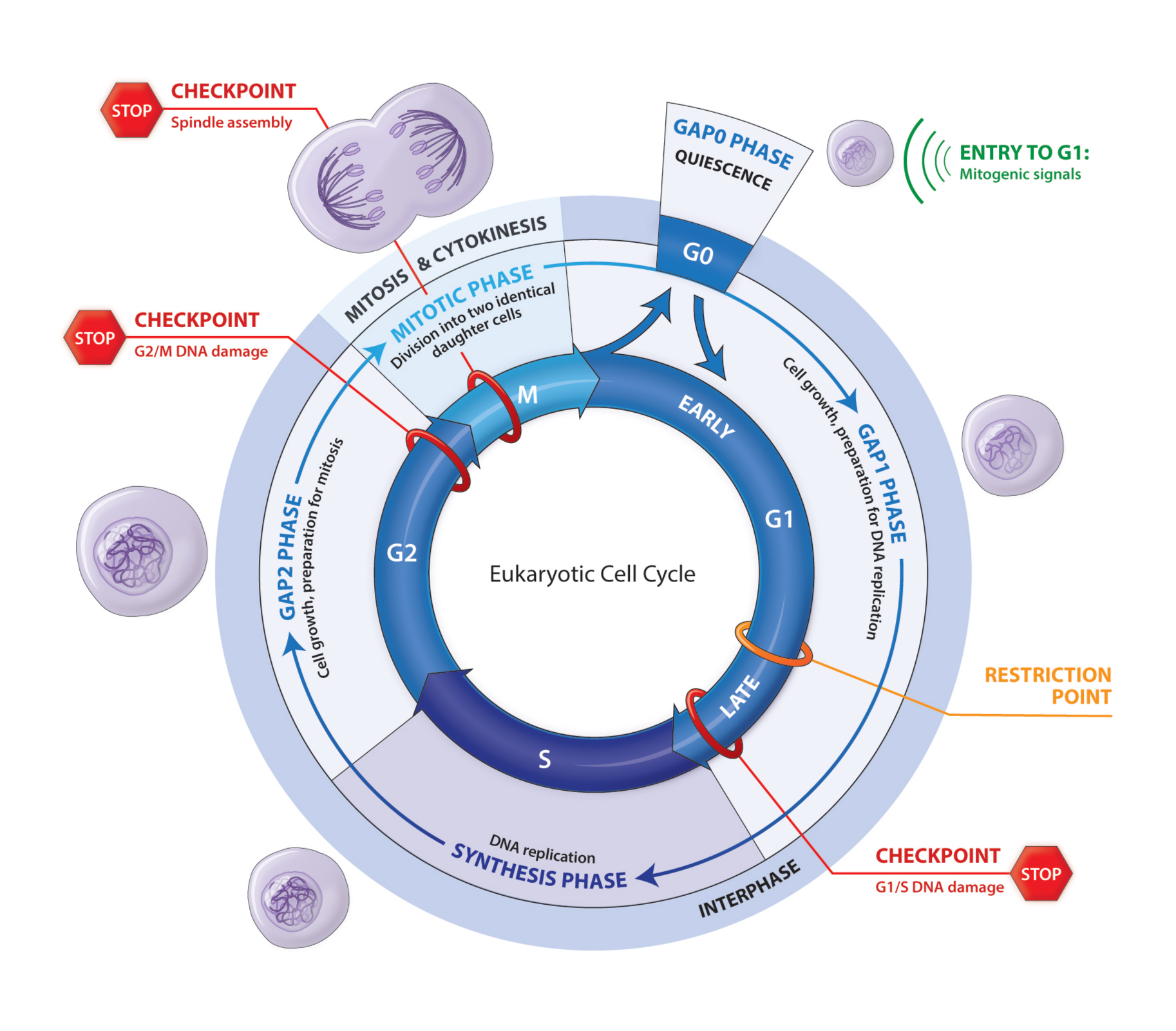
The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle — SLK ART
Definition. Cell-cycle proteins are the proteins involved in regulation and maintenance of the cell cycle of eukaryotic cells. These include kinases and cyclins that regulate movement between the.

Cell Cycle Regulation Cyclins and CDKs PraxiLabs
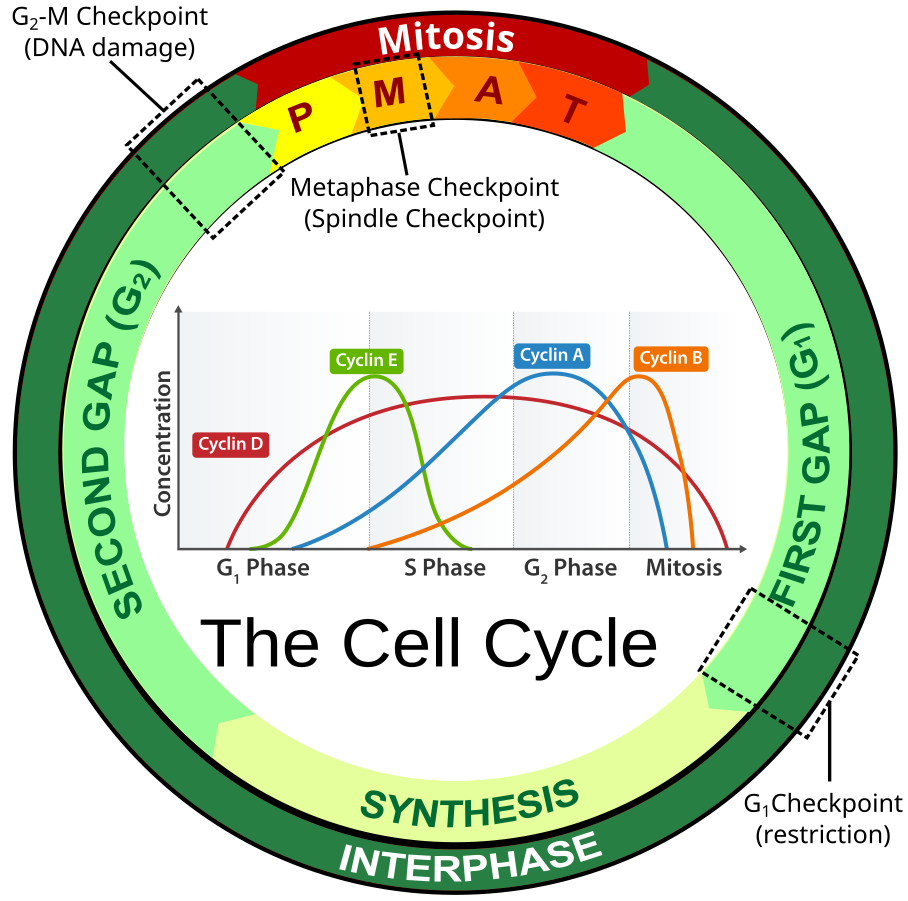
After the cell moves to the next stage of the cell cycle, the cyclins that were active in the previous stage are degraded. Figure 10.3C. 1 10.3 C. 1: Cyclin Concentrations at Checkpoints: The concentrations of cyclin proteins change throughout the cell cycle. There is a direct correlation between cyclin accumulation and the three major cell.
Cell Division Biology OER
This allows these proteins - such as cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases - to act as "stop points." If the cyclins or cyclin-dependent kinases don't give the go-ahead, the cell cannot progress to subsequent stages of the cell cycle. Some examples of cell cycle regulation are given below. Cell Cycle Examples

Cell Cycle Definition, Phases, Regulation, Checkpoints
Cell cycle entry and progression. Before S phase, in the prereplicative G1 phase, there is a decision window during which cells can commit to initiate DNA replication and enter the cell cycle or.
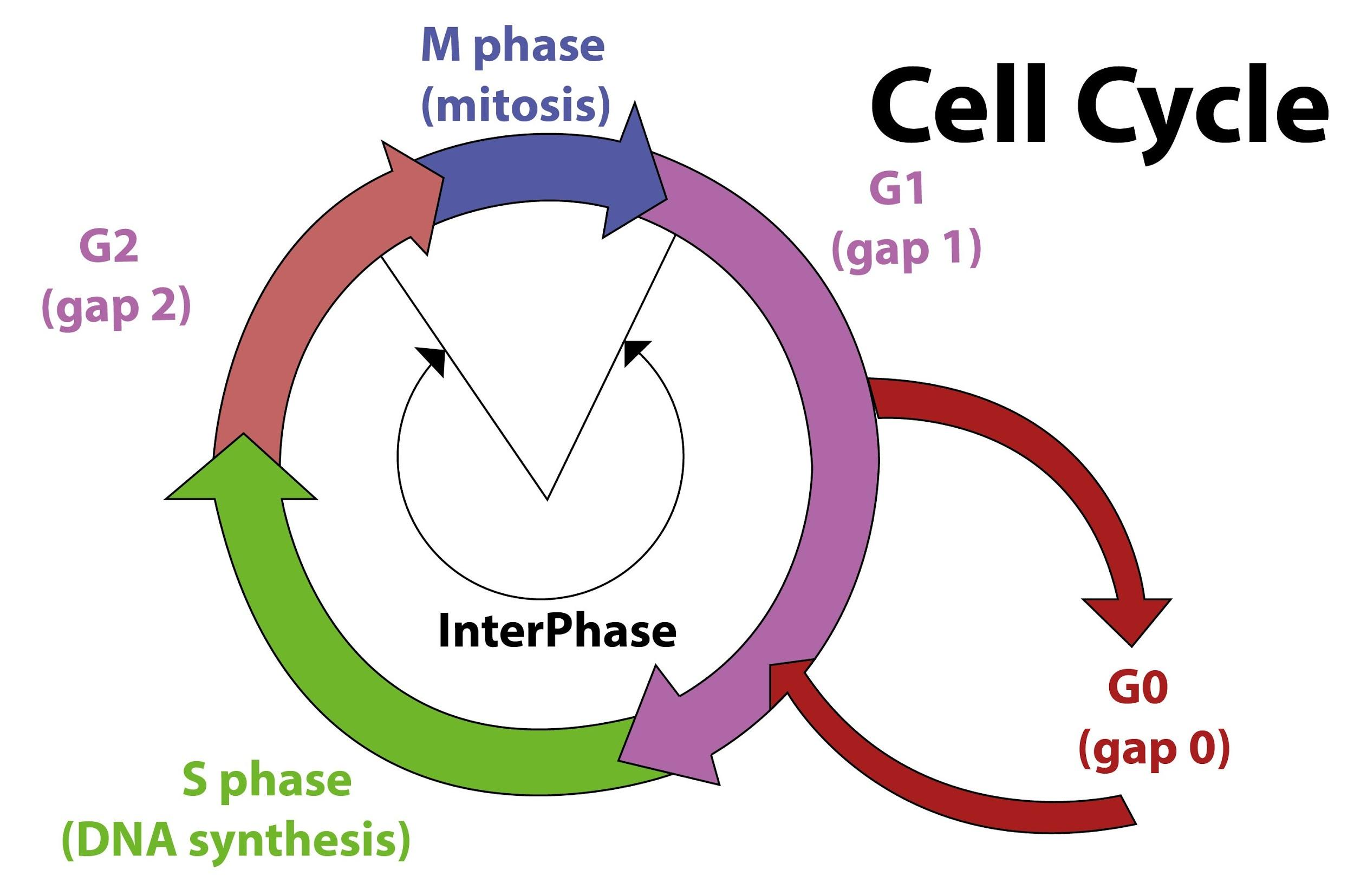
During the cell cycle, RNA and protein synthesis takes place during
Mechanism discovered for the degradation of key cell-cycle regulators. The molecular mechanism governing the destruction of key cell-cycle proteins, D-type cyclins, has been elucidated.
Focus on the Cell Cycle
Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) lie at the heart of eukaryotic cell cycle control, with different cyclin-CDK complexes initiating DNA replication (S-CDKs) and mitosis (M-CDKs)1,2. However, the.
PPT REGULATION OF CELL CYCLE BY PROTEIN KINASES PowerPoint
Positive Regulation of the Cell Cycle. Two groups of proteins, called cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks), are termed positive regulators. They are responsible for the progress of the cell through the various checkpoints. The levels of the four cyclin proteins fluctuate throughout the cell cycle in a predictable pattern (Figure 10.12.
Cell Cycle Definition, Phases, Regulation, Checkpoints
Cell Cycle Regulation 1. Cyclins. Cyclins are a group of proteins that together work to regulate different phases of the cell cycle as core regulators. These proteins regulate the various phases of the cell cycle by either activating the cyclin-dependent kinases or by activating some other enzymes or complexes.